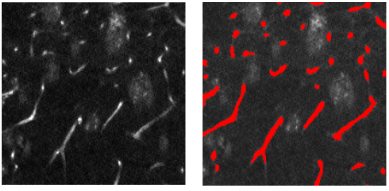
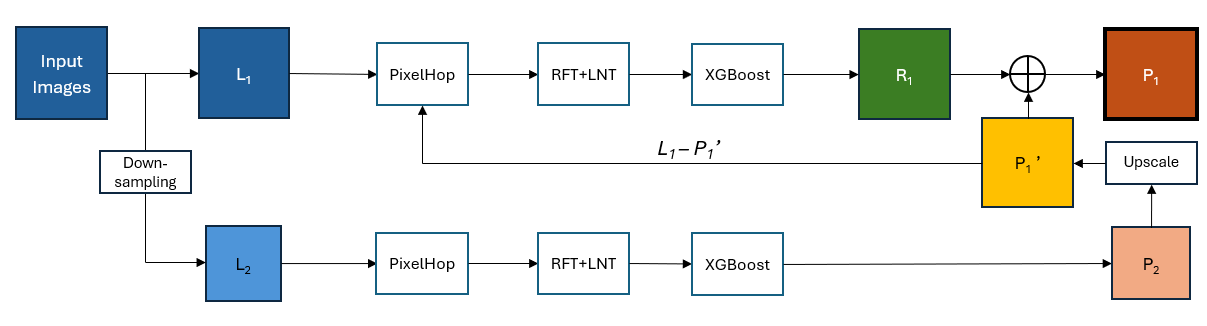
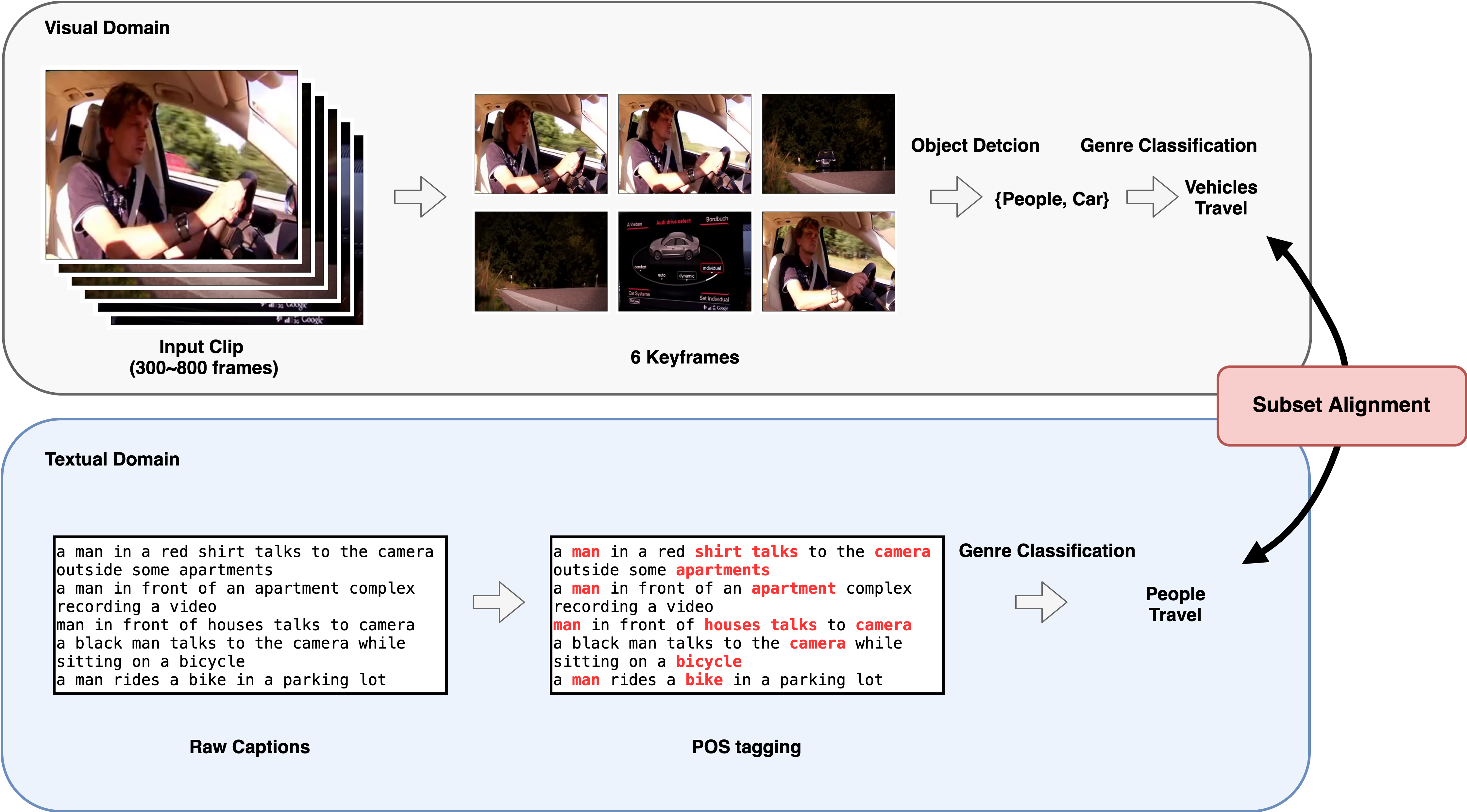
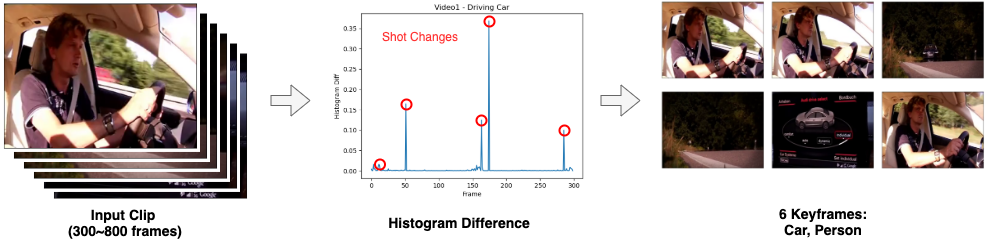
Congratulations to Haiyi Li for passing her Qualifying Exam
Congratulations to Haiyi Li for passing her Qualifying Exam! Her thesis proposal is titled “Interpretable and Lightweight Transfer Learning: Methodologies and Applications.” Her Qualifying Exam Committee members include Jay Kuo (Chair), Antonio Ortega, Anand Joshi, Justin Haldar, and Jernej Barbic (Outside Member). Here is a summary of her thesis proposal:
Transfer learning leverages knowledge from a labeled source domain to improve performance in an unlabeled or sparsely labeled target domain. Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) addresses this challenge by mitigating domain shift without target labels. Although deep learning–based UDA methods achieve strong performance, they typically require heavy computation, lack interpretability, and are prone to overfitting, limiting their practicality in resource-constrained settings.
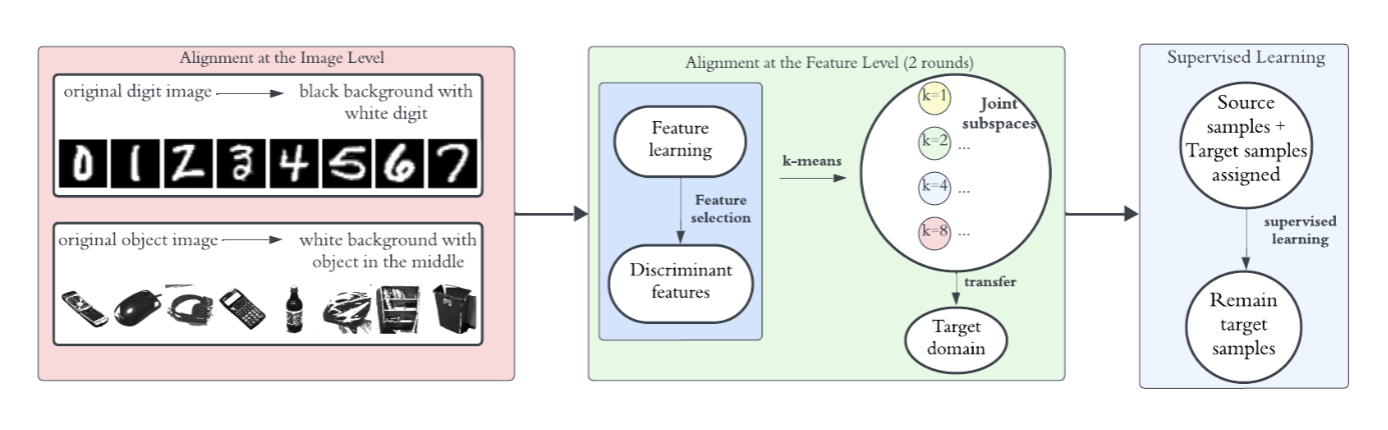
This research proposes a sequence of green learning–oriented transfer learning frameworks that emphasize efficiency, generalizability, and interpretability without relying on deep neural networks. We first introduce Green Image Label Transfer (GILT), a lightweight and transparent statistical alignment framework that decomposes UDA into three interpretable phases: joint discriminant subspace learning, source-to-target label transfer, and supervised learning in the target domain. GILT demonstrates effective cross-domain label transfer with low computational cost and compact models.
Building on GILT, we propose Interpretable and Lightweight Transfer Learning (ILTL), which employs a two-stage cascaded alignment strategy combining image-level and feature-level alignment in a shared discriminative subspace. Through multi-round label transfer and class-wise refinement, ILTL achieves competitive accuracy while further improving interpretability and efficiency.
To capture relational structure among samples, we extend this paradigm to a Graph-based Label Transfer (GLT) framework. GLT integrates statistical alignment with adaptive label-wise graph learning and entropy-aware iterative label propagation using a non-parametric GraphHop mechanism. A multi-fold validation–driven entropy filtering strategy enables reliable pseudo-label selection, resulting in robust and transparent transfer under domain shift.
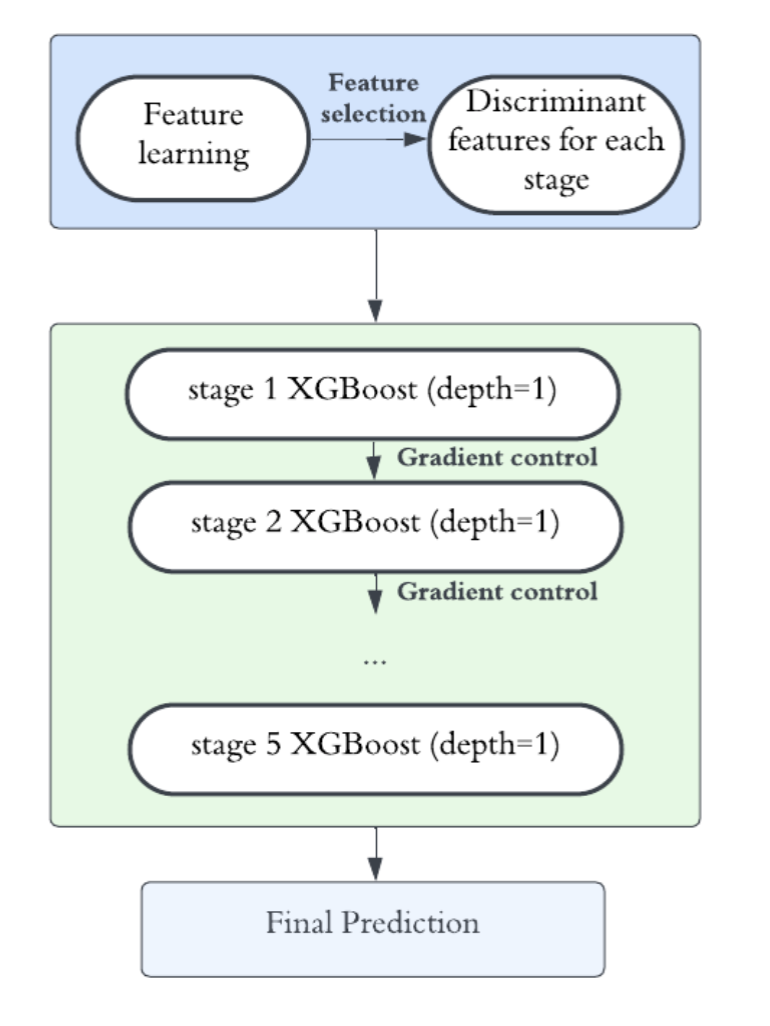
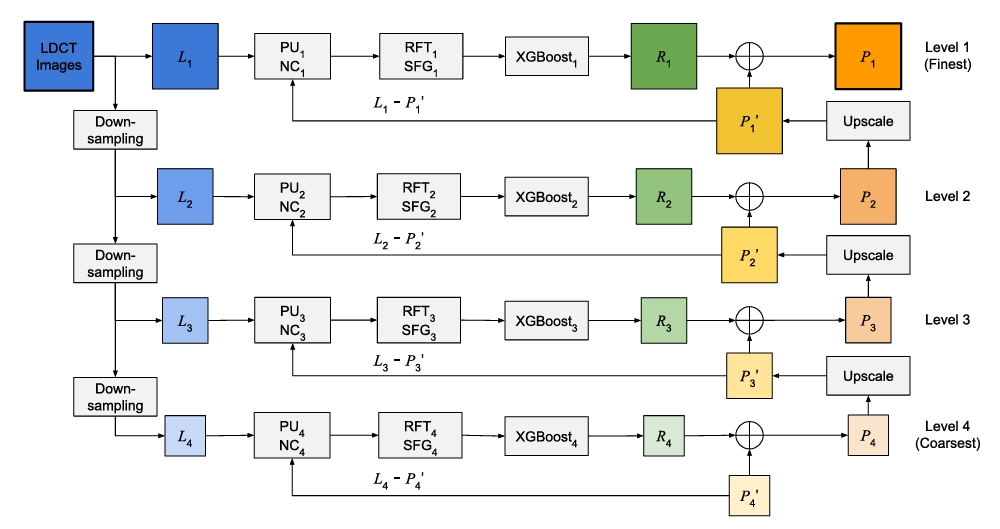
Finally, to address the computational bottleneck of decision learning [...]