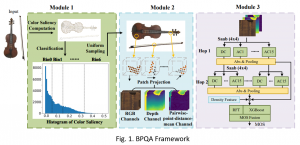
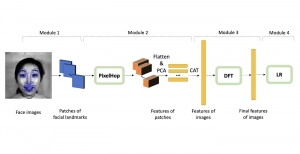
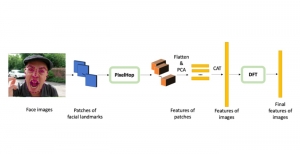
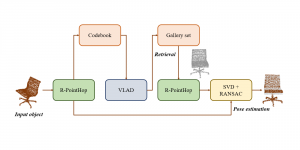
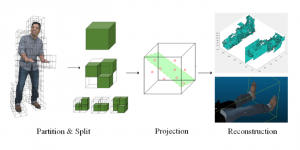
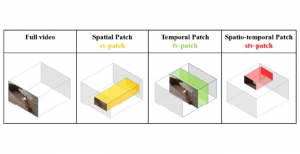
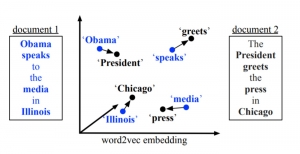
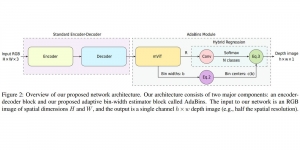
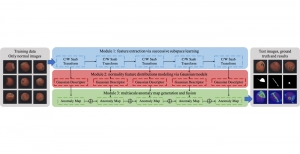
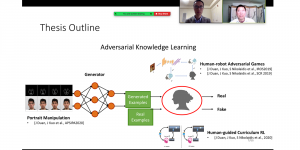
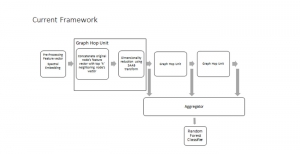
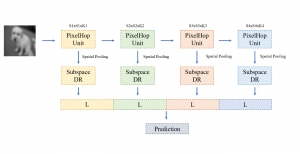
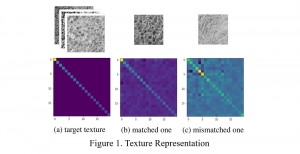
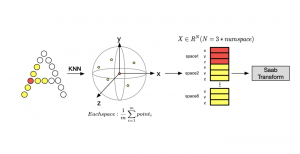
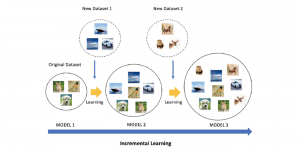
Seven MCL members attended the Viterbi PhD hooding ceremony on Thursday, May 15, 2014, from 8:30-11:00 a.m. in the Bovard Auditorium. They were Martin Gawecki, Harshad Kadu, Hyunsuk Ko, Kuan-Hsien Liu, Tsung-Jung Liu, Sanjay Purushotham and Xue Wang. Congratulations to them and their families for their accomplishments in completing their PhD program at USC.
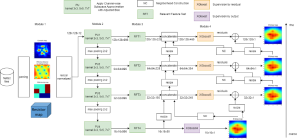
Martin Gawecki received a B.S. degree in Electrical Engineering from the University of California, Riverside (UCR) and an M.S. degree in Electrical Engineering from the University of Southern California (USC). Since 2009, he has been a member in the Media Communications Lab at USC, participating in the fields of statistical signal processing, machine learning, and time series analysis. His dissertation, entitled “A Signal Processing Approach to Robust Jet Engine Fault Detection and Diagnosis,” discusses the algorithms that can be used to advance engine health monitoring (EHM) with respect to data from vibration, acoustic, and classical (gas path) sensors. Done in conjunction with the Pratt-Whitney Institute for Collaborative Engineering (PWICE), his work demonstrates the superiority of vibration over acoustic sensors and showcases the ability of machine learning methods to assess performance of real engines based on fully simulated training data.
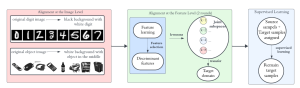
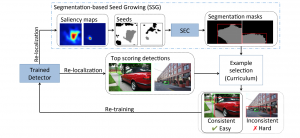
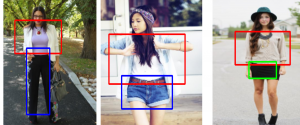
Harshad Kadu received his Bachelor’s degree from National Institute of Technology, Nagpur in 2008 and Master’s degree from University of Southern California, Los Angeles in 2011. Since then he has been pursuing his PhD in Electrical Engineering with Media Communications Lab at USC. His research interests include 3D human motion capture data analysis, image and music information processing, computer vision and statistical machine learning. His thesis titled ‘Advanced Techniques for Mocap Data Classification and Text Detection’ presents multi-resolution string representation based temporal and spatial domain techniques for human action recognition. His recent work on text detection demonstrates the effectiveness of multi-level detector and classifier fusion for textual pattern recognition in natural scenes and compound images.
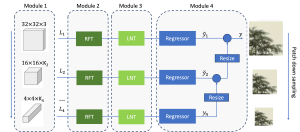
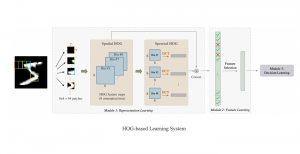
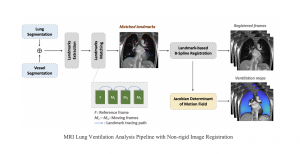
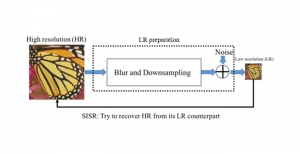
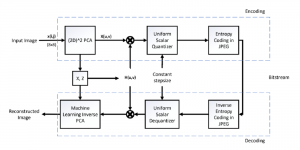
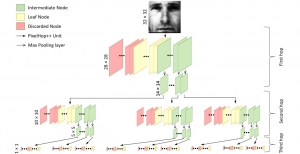
Hyunsuk Ko received the B.S. and M.S. degrees from the Department of Electrical Engineering, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea, in 2006 and 2009, respectively. From 2009 to 2010, he was a software engineer at Samsung Electronics, Suwon, Korea. He joined in the Media Communication Lab at USC for pursuing Ph.D degree since 2010. His thesis, entitled “3D Image Processing via a Structured Learning System”, discusses the 3D image quality assessment using 2-stage fusion system adopting machine leaning approach and related database as well. His research interests also include 3D view synthesis, 3D video coding, big data analysis, and stereo vision.
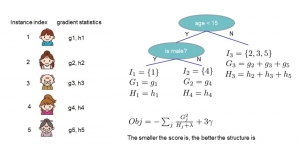
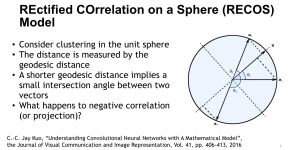
Kuan-Hsien Liu received the B.S. degree in Electrical Engineering from National Central University, Taiwan, and the M.S. degree in Communication Engineering from National Taiwan University, Taiwan, respectively. Since 2010, he has been a member of Media Communications Lab., led by Prof. C.-C. Jay Kuo in Ming Hsieh Department of Electrical Engineering, USC. His research interests include computer vision, machine learning, face recognition, and facial age estimation. His dissertation title is “Facial Age Grouping and Estimation via Ensemble Learning”. In his work, age estimation algorithms based on machine learning have been proposed and validated on well-known databases.
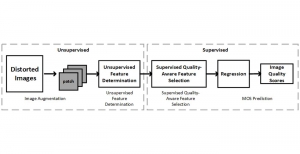
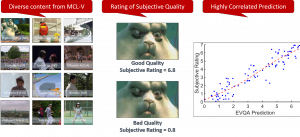
Tsung-Jung Liu received the B.S. degree in Electrical Engineering from National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan, and the M.S. degree in Communication Engineering from National Taiwan University, Taiwan, respectively. Since 2010, he has been a member of Media Communications Lab in Ming Hsieh Department of Electrical Engineering, USC. He was a Visiting Student with the School of Computer Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore in summer 2011. His dissertation title is “A Learning-based Approach to Image Quality Assessment”. In his work, several image quality assessment algorithms based on learning have been proposed, including full-reference (FR) and no-reference (NR) methods. He also did some work on subjective database evaluation and video quality assessment. His research interests cover machine learning, perceptual signal processing, and visual quality assessment.
Sanjay Purushotham received a B.Tech degree in Electronics and Communications Engineering from National Institute of Technology Karnataka, India and an M.S degree in Electrical Engineering from University of Southern California (USC). Since 2009, he has been a research assistant in the Media Communications Lab (MCL) at USC advised by Prof. C.-C. Jay Kuo, and has been working on various research areas including multimedia data mining, machine learning, computer vision and optimization algorithms. His thesis, entitled “Advanced Learning Techniques for Annotation, Retrieval and Recommendation in Social Multimedia Networks” discusses advanced algorithms and systems for solving multimedia problems in social networks. His work demonstrates that multimedia mining and modeling social network information are both important for addressing many of the ‘Big Data’ problems in today’s highly networked world.
Xue Wang received her B.S. degree in Applied Physics and M.S. degree in Optical Engineering from the Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China in 2007 and 2009, respectively. In August 2009, she became a Ph.D. student in Dept. of Electrical Engineering at University of Southern California (USC); and since January 2011, she has been with Media Communications Lab. Her research interests lie in the inetrdiscipline of biomedical information processing, machine learning, and computer vision and her dissertation discusses about applying machine learning based