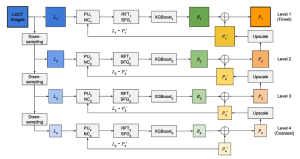
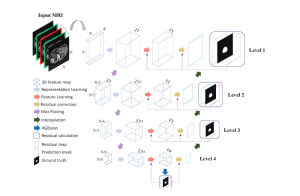
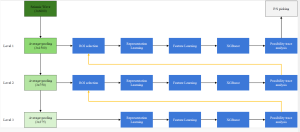
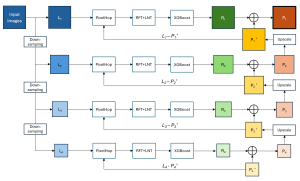
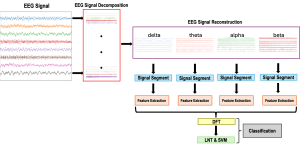
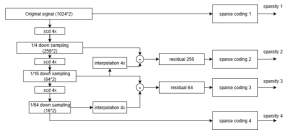
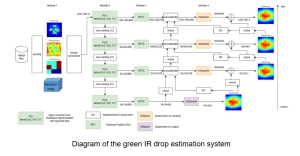
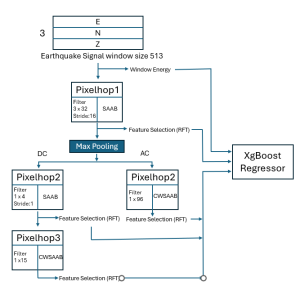
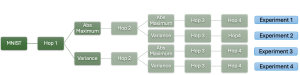
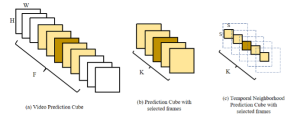
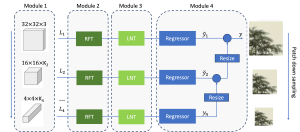
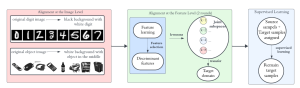
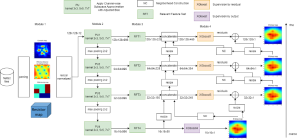
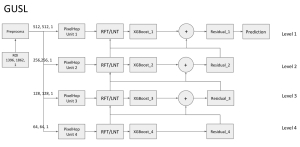
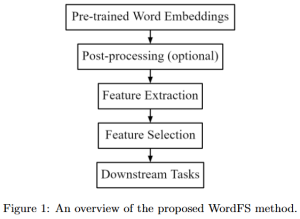
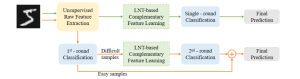
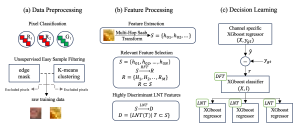
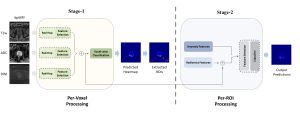
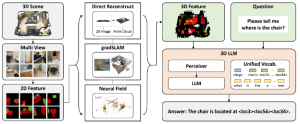
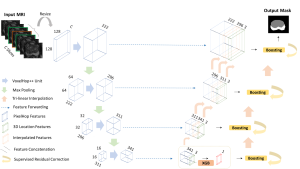
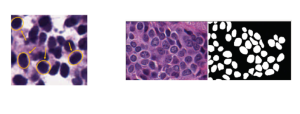
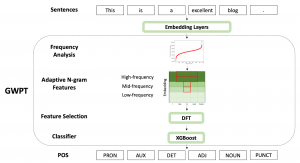
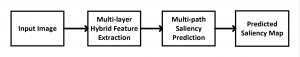
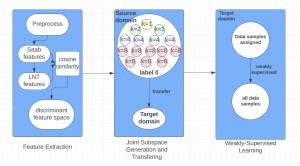
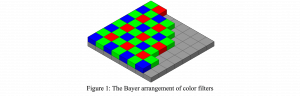
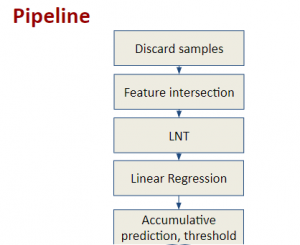
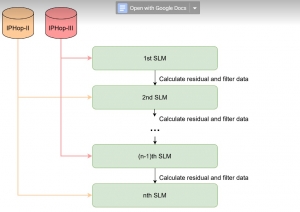
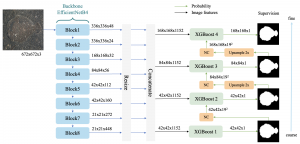
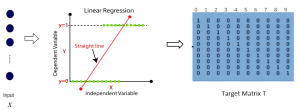
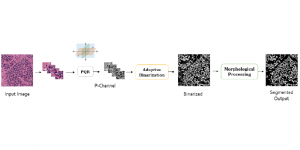
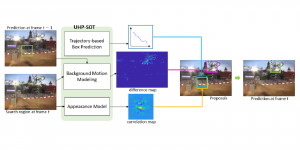
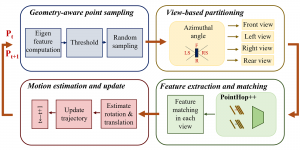
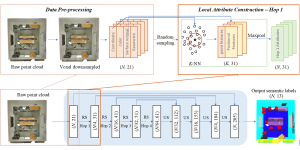
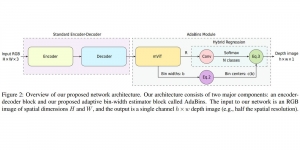
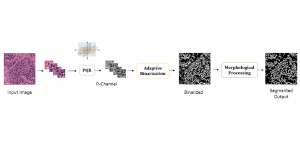
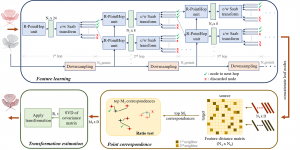
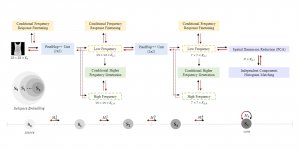
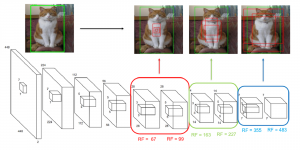
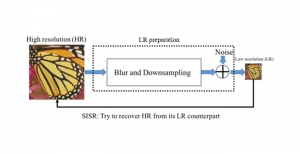
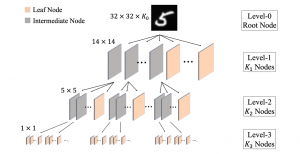
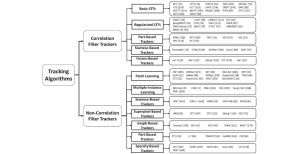
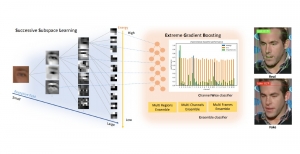
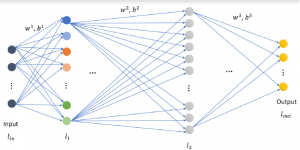
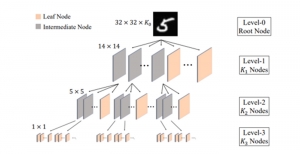
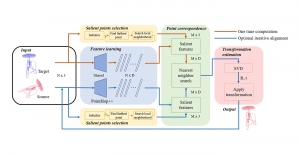
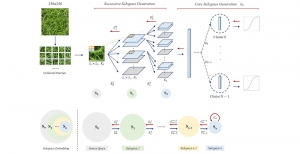
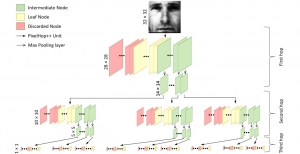
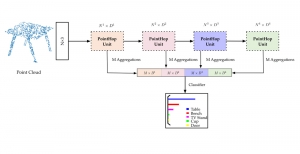
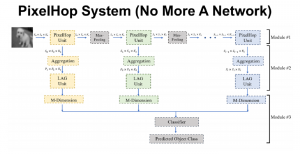
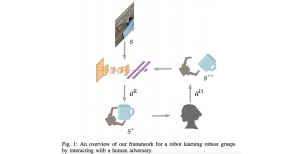
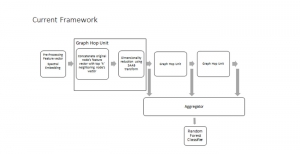
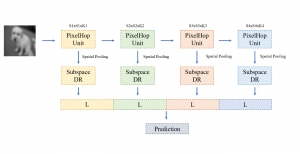
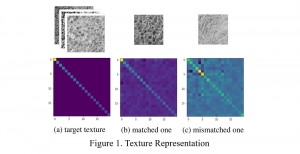
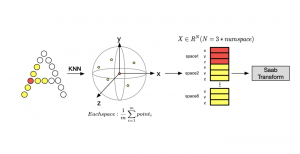
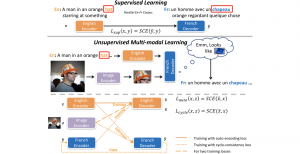
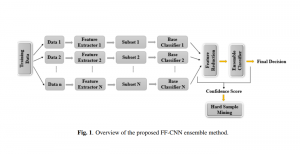
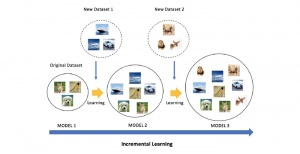
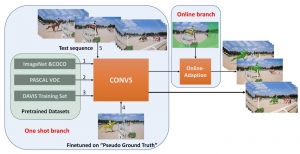
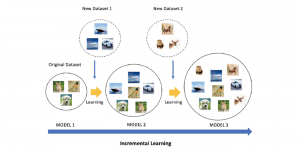
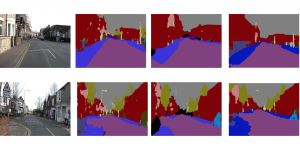
As a fundamental Computer vision problem, image denoising aims at reducing noise images to improve resolutions. As a sub-topic of image restoration, image denoising not only has wide applications in practical problems, but also can be important pre-processing procedures for other CV or NLP problems.
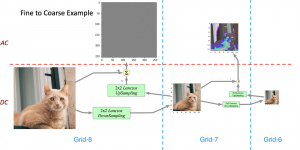
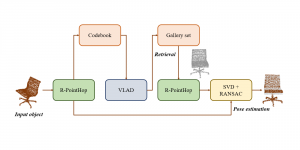
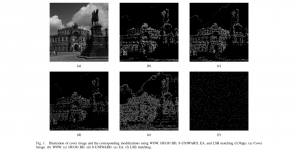
Traditionally, algorithms by patch-wise denoising, like Non-local Mean and BM3D, usually assume the noise are Gaussian noise try to reduce noise by the randomness of noise and signal preservation across similar patches. After CNN architecture introduced to CV field, similar to other image restoration problems like super-resolution, deblurring, and dehazing, denoising problem also developed out CNN-based methods, with two main streams: one focus more on pixel-wise restoration and the other cares more about overall pleasure. Besides, combining different image restoration problems together, that building a more general model which can work on multiple image restoration problems gradually obtained more attention.
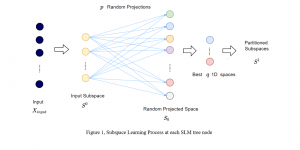
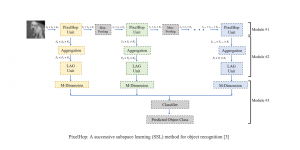
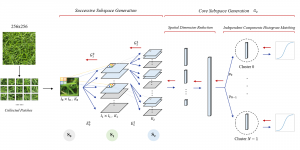
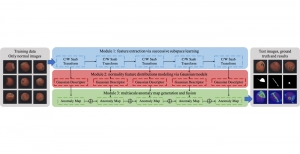
With better performance achieved in denoising problem, more and more algorithms suffer from the model size and reference speed. We would like to introduce SSL principle to tackle denoising problem with comparable performance while with higher efficiency in the future.
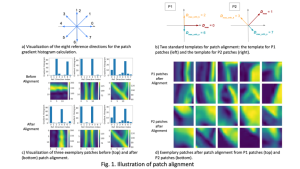
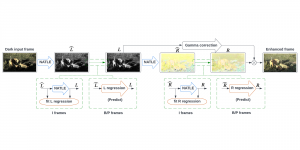
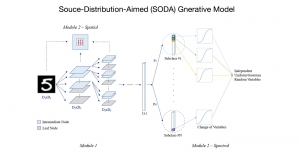
Image credit: Dabov, Kostadin, et al. “Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering.” IEEE Transactions on image processing 16.8 (2007): 2080-2095.